Growing Plant Stages Explained: From Seed to Bloom
The Marvelous Metamorphosis: A Journey Through the Stages of Plant Growth
Plants, the silent architects of our planet's verdant tapestry, embark on an extraordinary journey of transformation from tiny seeds to towering giants. Their growth, a symphony of intricate processes orchestrated by nature, unfolds across three distinct stages: germination, vegetative growth, and reproductive growth. Each stage is characterized by unique developmental milestones, shaping the plant's form and function.
The Growing Plant Stages
Germination: The Spark of Life
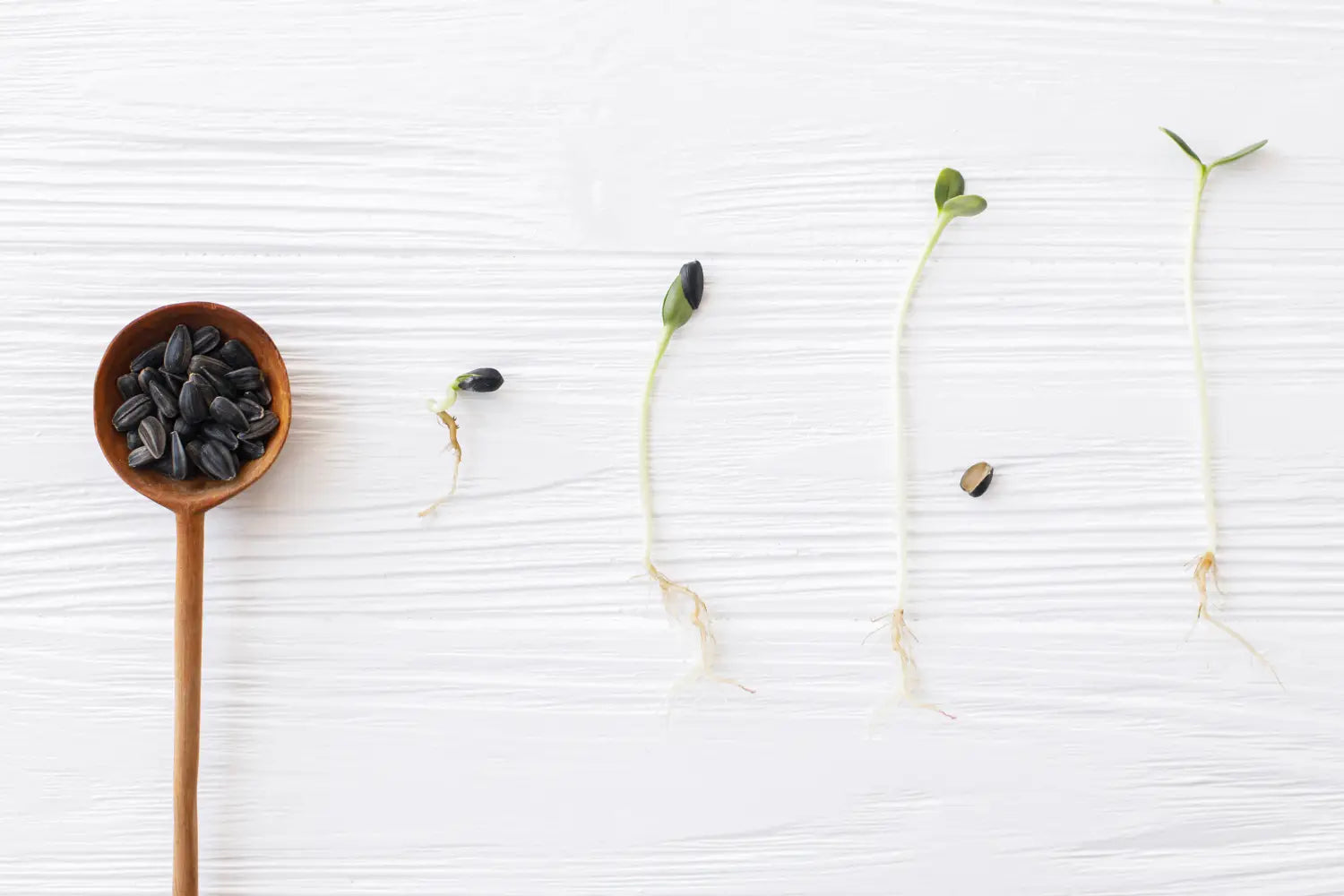
The genesis of a plant's existence lies in the humble seed, a vessel of dormant potential. Within its protective coat, a miniature plant lies in wait, poised to awaken to the symphony of life. The trigger for this awakening is germination, the process by which a seed imbibes water and swells, initiating the first stirrings of growth.
Root Emergence: Anchoring in the Earth
As the seed awakens, its first act is to send forth a delicate root, the radicle, anchoring the plant to the life-giving soil. This tenacious root, a pioneer in the subterranean realm, embarks on a quest for sustenance, seeking the water and nutrients that will fuel the plant's growth.
Shoot Emergence: Reaching for the Sun
While the root delves into the depths, its counterpart, the plumule, emerges from the seed, reaching upwards towards the celestial beacon of life: the sun. This delicate shoot, bearing the promise of photosynthesis, seeks the radiant energy that will drive the plant's metabolic processes.
Cotyledon Unfolding: The First Glimpse of Green
The cotyledons, the plant's first leaves, unfold from the seed, their verdant hues heralding the plant's entry into the photosynthetic world. These embryonic leaves, though temporary, play a pivotal role, providing the plant with its first taste of nourishment from the sun's energy.
Vegetative Growth: The Symphony of Expansion
With the foundations laid, the plant embarks on a period of exuberant growth, a stage known as vegetative growth. This dynamic phase is characterized by rapid cell division, resulting in the expansion of leaves, stems, and roots.
Leaf Development: Unveiling the Engines of Photosynthesis
The leaves, the plant's photosynthetic factories, unfurl their delicate expanses, transforming sunlight into energy. As new leaves emerge, the plant's capacity for photosynthesis expands, fueling its growth and providing sustenance for the entire organism.
Stem Elongation: A Tower Reaching for the Sky
The stem, the plant's structural backbone, stretches upwards, providing support for the expanding leaves and carrying them toward the sun's embrace. This elongation not only optimizes photosynthesis but also allows the plant to compete for light and space in the crowded plant community.
Root Expansion: Anchoring and Nourishing the Growing Giant
As the plant ascends towards the sun, its roots delve deeper into the soil, anchoring it firmly against the elements and expanding its reach for water and nutrients. This intricate subterranean network sustains the plant's growth, ensuring its access to the vital resources it requires.
Reproductive Growth: The Legacy of Life
Having established itself as a thriving member of the plant kingdom, the plant enters the final stage of its life cycle: reproductive growth. This phase is dedicated to ensuring the perpetuation of its species, a testament to the enduring cycle of life.
Flower Bud Formation: The Promise of Blooms
Along the stem, delicate protuberances emerge, the heralds of the plant's reproductive potential: flower buds. These buds, cradles of life, hold within them the promise of vibrant blooms, attracting pollinators and setting the stage for the miracle of fertilization.
Flowering: A Symphony of Color and Fragrance
The flower buds, bursting with anticipation, unfurl their petals, revealing a kaleidoscope of colors and an intoxicating array of fragrances. These ephemeral masterpieces, nature's exquisite artistry, serve as beacons for pollinators, inviting them to partake in the delicate dance of reproduction.
Pollination: A Dance of Life and Renewal
Amidst the vibrant tapestry of blooms, a ballet unfolds pollination. Windborne pollen, the messengers of life, flutter from flower to flower, carrying the genetic material that will ensure the next generation of plants.
Fertilization: The Fusion of Life
Upon reaching the stigma of the receptive female flower, pollen grains embark on a remarkable journey down the style, reaching the ovules nestled within the ovary. There, in the heart of the flower, fertilization occurs, the fusion of male and female genetic material, giving rise to a new life.
Fruit and Seed Development: The Promise of the Future
As the plant transitions from its reproductive phase to the final stages of its life cycle, it enters a crucial period of fruit and seed development, embodying the promise of the future.
The Transformation of the Ovary
In the heart of the flower, the ovary, once a haven for the ovules, undergoes a remarkable transformation. Fueled by the process of fertilization, the ovary begins to swell and enlarge, its walls thickening to enclose and protect the developing seeds.
The Seeds Take Shape
Within the confines of the ovary, the fertilized ovules embark on a journey of maturation, transforming into seeds, the bearers of the plant's genetic legacy. These tiny capsules, each encased in a protective coat, harbor the potential for new life, a promise to perpetuate the species.
The Encapsulation of Nutrients
As the seeds mature, they accumulate energy-rich compounds, such as starches and oils, providing nourishment for the embryonic plant within. These vital reserves will fuel the seedling's initial growth upon germination, ensuring its survival in the competitive world.
The Fruits Emerge
In tandem with seed development, the ovary itself undergoes a metamorphosis, evolving into a fruit, nature's ingenious packaging for the seeds. Fruits, adorned with vibrant hues and enticing aromas, serve as beacons for dispersers, enticing them to partake in the plant's reproductive strategy.
Dispersal Mechanisms: Scattering Life's Bounty
Plants employ a diverse array of dispersal mechanisms to ensure their seeds reach far and wide, expanding their geographical range and colonizing new habitats. Wind, water, and animals all play a role in this grand dispersal dance, each contributing to the perpetuation of plant life.
Seeds: The Promise of Renewal
Upon reaching a suitable environment, the seeds, now armed with their nutrient reserves and protected by their coats, enter a state of dormancy, awaiting the opportune moment to awaken. When conditions are favorable, the seeds germinate, giving rise to new seedlings, the embodiment of hope and renewal.
The development of fruits and seeds represents a culminating act in the plant's life cycle, a testament to its resilience and adaptability. Through the dispersal of seeds, plants extend their reach, colonizing new territories and ensuring their survival in an ever-changing world. Thus, fruits and seeds embody the promise of the future, carrying the potential for new life and the perpetuation of the plant kingdom's rich diversity.
Senescence and Dormancy: Preparing for Rest
As the seasons change, plants undergo a series of physiological changes to prepare for the harsh conditions of winter. These changes include senescence and dormancy.
Senescence is the natural aging process of plants. It is characterized by a decline in plant growth, metabolism, and reproductive capacity. The leaves of senescent plants often turn yellow or brown and fall off. This is because the plant is reabsorbing nutrients from the leaves back into the stem and roots.
Dormancy is a state of reduced metabolic activity in plants. It is a way for plants to conserve energy and survive unfavorable conditions, such as cold temperatures and lack of water. During dormancy, plants may lose their leaves, and their stems may become woody.
Senescence and dormancy are both important processes that help plants to survive in a changing environment.
Senescence allows plants to reabsorb nutrients from their leaves and stems, which can be used to support new growth in the spring. It also helps to reduce the amount of surface area that the plant has to expose to the cold, dry air of winter.
Dormancy helps plants to conserve energy during times of stress. By slowing down their metabolism, plants can reduce their need for water and nutrients. This can help them to survive even in the harshest of conditions.
The timing of senescence and dormancy is controlled by a number of factors, including day length, temperature, and the availability of water.
In general, plants will start to senesce and enter dormancy as the days get shorter and the temperatures get colder. However, the exact timing of these processes will vary depending on the species of plant.
Senescence and dormancy are reversible processes.
When conditions improve, plants will come out of dormancy and start to grow again. The timing of this process is also controlled by a number of factors, including day length, temperature, and the availability of water.