Hydroponic Farming: Cultivating the Future of Agriculture
In a world grappling with food security, environmental concerns, and resource scarcity, hydroponic farming has emerged as a beacon of hope, offering a sustainable and efficient approach to agriculture.
What is Hydroponic Farming?
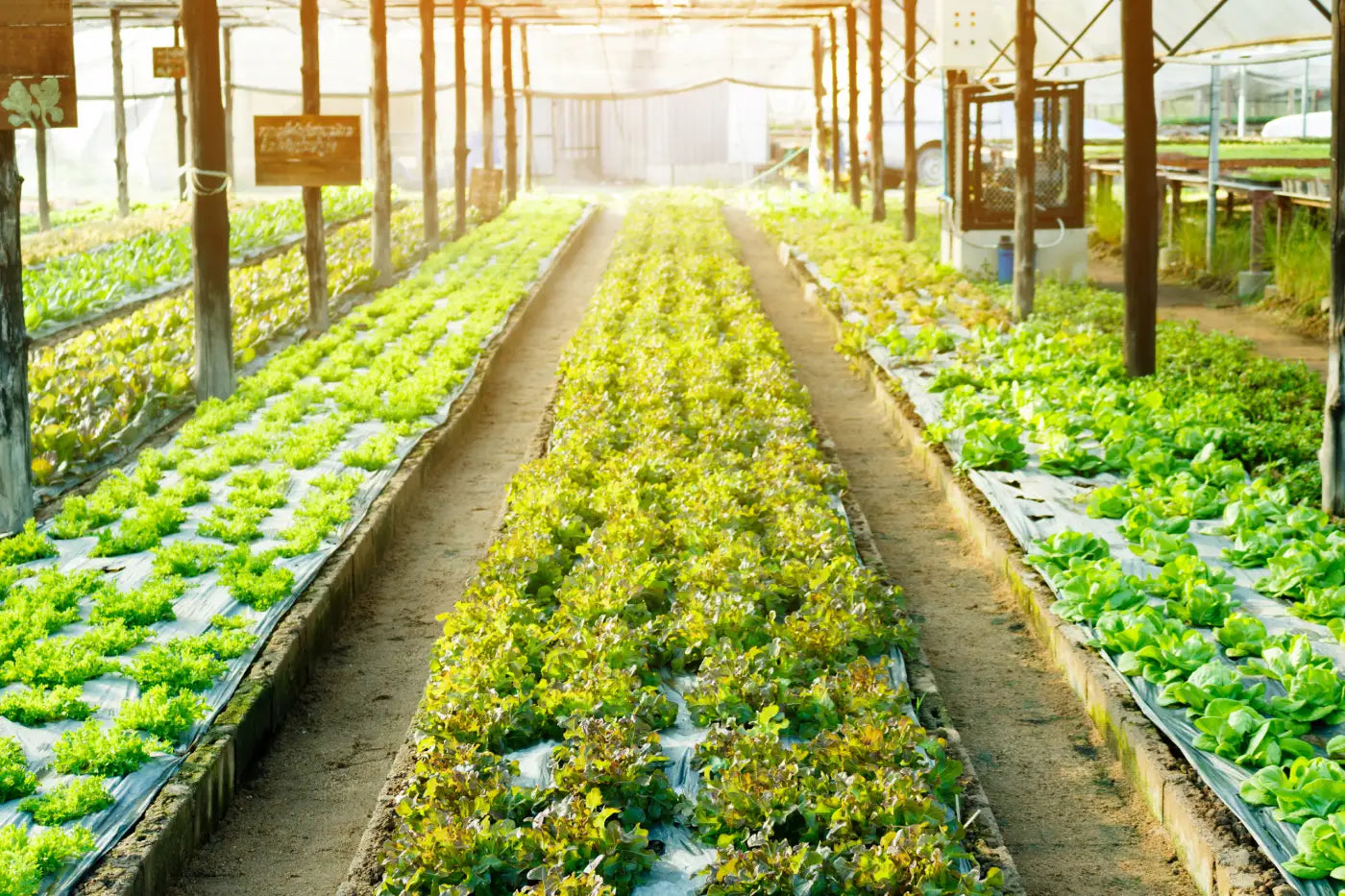
Hydroponic farming is a method of growing plants without soil. Unlike traditional soil-based methods, hydroponic farming eliminates the need for soil, relying instead on nutrient-rich water solutions to nourish plants. The roots of the plants are submerged or periodically exposed to this nutrient solution, allowing them to absorb the necessary elements directly. This soilless technique not only conserves water and reduces the risk of soil-borne diseases but also enables year-round production in controlled environments, regardless of external weather conditions.

There are various hydroponic systems, such as:
Deep Water Culture (DWC): Plants are suspended in a nutrient solution with their roots immersed.
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT): A thin film of nutrient-rich water flows through a sloped channel, and plants' roots are exposed to this film.
Aeroponics: Roots are suspended in the air, and a mist or spray of nutrient solution is applied periodically.
Ebb and Flow (or Flood and Drain): Plants are periodically flooded with the nutrient solution and then drained.
Hydroponic farming offers several advantages, such as efficient use of water (as it recirculates in systems), precise control over nutrient levels, faster growth rates, and the ability to grow plants in areas with limited access to fertile soil. It's commonly used in urban agriculture, research facilities, and in areas with challenging environmental conditions.
Unveiling the Benefits of Hydroponic Farming
The benefits of hydroponic farming extend far beyond its water-saving prowess. By eliminating soil as a growing medium, hydroponics offers a multitude of advantages, including:
Water Conservation: It uses significantly less water compared to traditional soil-based agriculture because the water in hydroponic systems is recycled and reused.
Controlled Environment: Hydroponic systems allow precise control over environmental factors like temperature, humidity, and light. This control optimizes plant growth and can extend growing seasons.
Higher Yields in Less Space: Hydroponic setups can produce higher yields per square foot than traditional farming due to optimized nutrient delivery and controlled conditions.
No Soil Required: It eliminates the need for fertile soil, making it viable for areas with poor soil quality or limited space for traditional farming.
Reduced Pesticide Use: Controlled environments can help minimize pests and diseases, reducing the need for pesticides and making the produce potentially safer and more eco-friendly.
Faster Growth Rates: Plants in hydroponic systems often grow faster because they receive an optimal balance of nutrients and ideal growing conditions.
Flexibility and Scalability: Hydroponic systems can be set up almost anywhere, from small indoor setups to large commercial operations, making them adaptable to various locations and scales.
Year-Round Production: With controlled environments, hydroponic farming allows for year-round crop production, irrespective of seasonal changes.
Nutrient Control: Growers have precise control over nutrient levels, ensuring plants receive the exact nutrients needed for optimal growth, potentially leading to higher-quality produce.
Environmental Benefits: It can reduce the carbon footprint associated with transportation since hydroponic systems can be set up closer to urban areas, reducing the distance food needs to travel.
These advantages make hydroponic farming an attractive option for sustainable agriculture, especially in regions facing challenges such as water scarcity or limited arable land.
How to Get Started with Hydroponic Farming?
Getting started with hydroponic farming involves several steps:
Research and Education: Familiarize yourself with hydroponic systems, different setups, and the specific requirements of the plants you want to grow. Understand the basics of nutrient solutions, pH levels, and environmental control.
Choose a System: Select a hydroponic system based on your space, budget, and the type of plants you want to grow. Systems like Deep Water Culture (DWC), Nutrient Film Technique (NFT), or simple container systems are good for beginners.
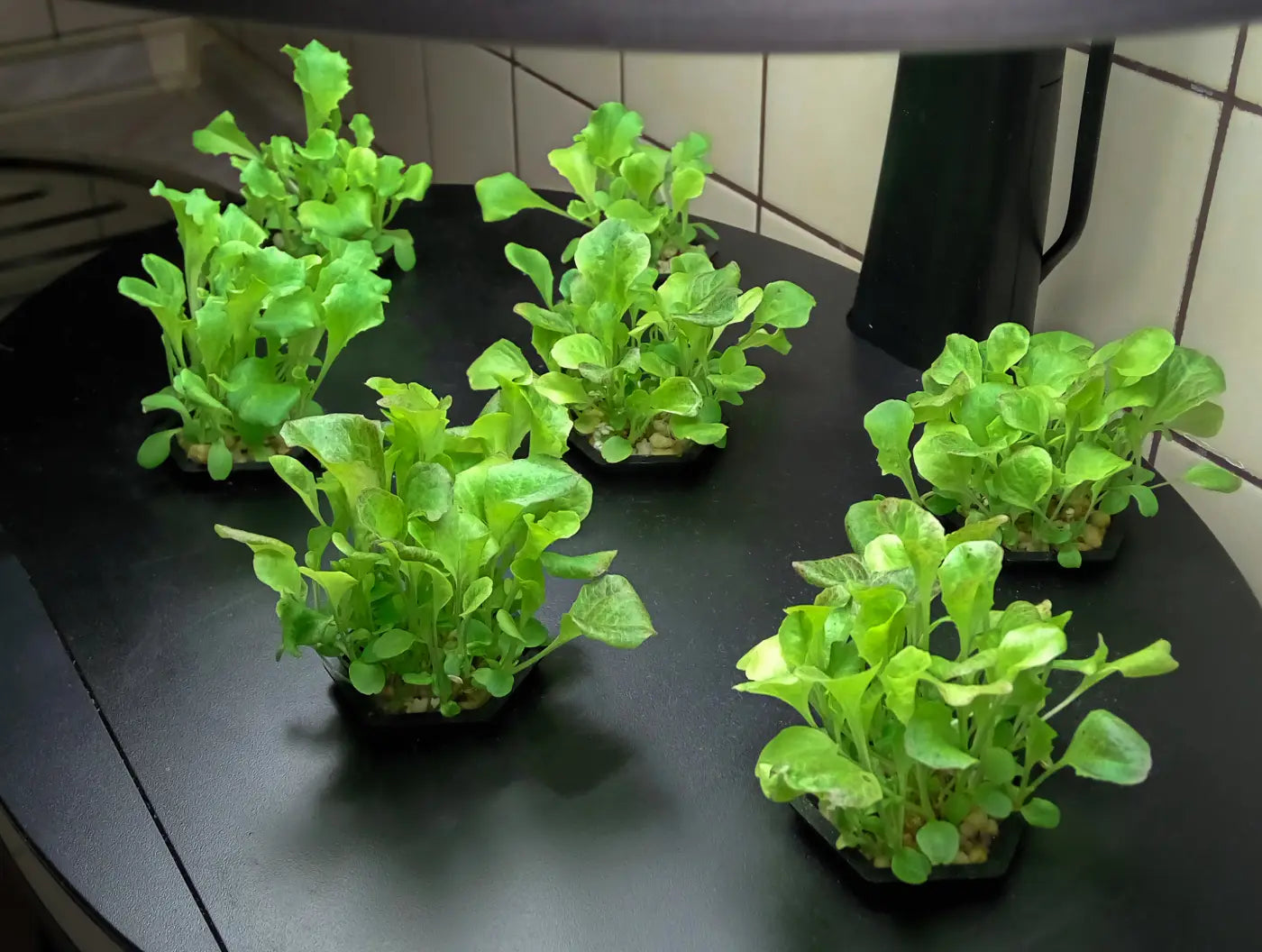
Select Plants: Decide which plants you want to grow. Some, like lettuce, herbs, and leafy greens, are well-suited for hydroponics, especially for beginners, due to their adaptability to various systems.
Gather Equipment: Acquire the necessary equipment, including containers or trays, a growing medium (like perlite, rockwool, or coconut coir), nutrient solutions, a pH testing kit, lighting (if growing indoors), and a pump (for some systems).
Set Up the System: Follow instructions or guides to set up your chosen hydroponic system. Ensure proper installation of pumps, reservoirs, and any necessary plumbing. Monitor for leaks and ensure everything is properly sealed.
Prepare the Nutrient Solution: Mix the nutrient solution according to the instructions provided. Ensure it has the appropriate balance of essential nutrients required for your plants.
Planting: Place your chosen plants into the growing medium in the hydroponic system. Ensure the roots are adequately submerged and the plants are stable.
Monitor and Maintain: Regularly check the pH and nutrient levels of the solution. Monitor the plants for signs of nutrient deficiencies, pests, or diseases. Adjust the environment as needed, including temperature, humidity, and light.
Harvest and Enjoy: As your plants grow, harvest them at the appropriate time. Enjoy the fresh produce you've grown through your hydroponic setup!
Learn and Improve: Keep learning from your experiences and consider experimenting with different plant varieties, nutrient solutions, or systems to improve your hydroponic farming skills.
Tips for Success with Hydroponic Farming
Here are a few tips for success with hydroponic farming:
Start Simple: Begin with a basic system and a few easy-to-grow plants. This allows you to understand the fundamentals before moving to more complex setups or challenging crops.
Quality Equipment and Supplies: Invest in good-quality equipment, nutrient solutions, and seeds or seedlings. Quality supplies can make a significant difference in plant growth and health.
Maintain Proper pH and Nutrient Levels: Regularly monitor and adjust the pH levels and nutrient concentrations in the solution to ensure plants receive the right balance of nutrients for optimal growth.
Lighting Matters: If you're growing indoors or in a place with limited natural light, invest in appropriate grow lights. Different plants have varying light requirements, so research the specific needs of your chosen plants.
Consistency is Key: Maintain consistent environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, and light cycles. Plants thrive on stability, so try to minimize fluctuations.
Proper Ventilation and Air Circulation: Ensure good airflow around your plants. This helps prevent mold, maintains proper CO2 levels, and strengthens plant stems.
Regular Maintenance: Clean your system regularly, check for clogs, and ensure all components are functioning correctly. This prevents issues and maintains a healthy growing environment.
Be Observant: Watch your plants closely. Learn to recognize signs of nutrient deficiencies, pests, or diseases early on and take action promptly.
Experiment and Learn: Don’t be afraid to experiment with different plant varieties, nutrient mixes, or growing techniques. Each experiment is a learning opportunity that can improve your skills.
Keep Learning: Hydroponic farming is a continuous learning process. Stay updated with the latest research, join forums or communities, and learn from other experienced growers to expand your knowledge.
Patience and Persistence: Like any form of farming, success in hydroponics often requires patience and persistence. Not every crop will be perfect, but each experience contributes to your expertise.
Remember, starting small and gradually scaling up allows you to learn and adapt as you go. Don’t get discouraged by initial setbacks—use them as opportunities to refine your methods and improve your yields.